Pharmaceutical intermediates are compounds used during the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). They are intermediate products in the chemical process that ultimately leads to the production of the final API. They can be used to make drugs for various therapeutic areas, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and central nervous system disorders. Pharmaceutical intermediates play a crucial role in determining the quality, purity, and stability of the final API, and therefore, their manufacturing and quality control are strictly regulated by government agencies. The proper selection and control of pharmaceutical intermediates is critical to ensuring the safety and efficacy of the final API.
-
![China 8-Azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-3-thiol, 8-Methyl-, (3-exo)- CAS848130-83-6 Manufacturer,Supplier](/uploadfile/202108/25/9c44bef167a3669f4ba475e225c1c816_small.jpg) 8-Azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-3-thiol, 8-Methyl-, (3-exo)- CAS848130-83-6He Maureen intermediates
8-Azabicyclo[3.2.1]octane-3-thiol, 8-Methyl-, (3-exo)- CAS848130-83-6He Maureen intermediates -
 1,2-Pentanediol CAS5343-92-01, 2 - butyl glycol is an important intermediate of azole fungicide c ring.
1,2-Pentanediol CAS5343-92-01, 2 - butyl glycol is an important intermediate of azole fungicide c ring. -
 Sisomicin CAS32385-11-8Used in the production of sisomicin sulfate or nanotubes sulfate for m star intermediates Used in pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacter and other gram-negative bacteria infection Used in pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacter and other gram-negative bacteria infection.
Sisomicin CAS32385-11-8Used in the production of sisomicin sulfate or nanotubes sulfate for m star intermediates Used in pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacter and other gram-negative bacteria infection Used in pseudomonas aeruginosa, enterobacter and other gram-negative bacteria infection. -
 (+)-Dibenzoyl-D-tartaric acid CAS17026-42-5use Widely used in chiral resolution amine compounds use Displacement of intestinal worm medicine intermediates of levamisole (for break).
(+)-Dibenzoyl-D-tartaric acid CAS17026-42-5use Widely used in chiral resolution amine compounds use Displacement of intestinal worm medicine intermediates of levamisole (for break). -
 4,6-Dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine CAS40497-30-1Used for the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates
4,6-Dihydroxy-2-methylpyrimidine CAS40497-30-1Used for the synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates -
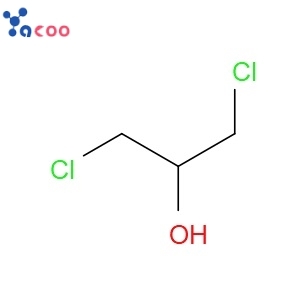 2-Methyl-4-nitroimidazole CAS696-23-1A hydroxyl ethyl nitrate azole (metronidazole) intermediate.
2-Methyl-4-nitroimidazole CAS696-23-1A hydroxyl ethyl nitrate azole (metronidazole) intermediate. -
![China 3-Morpholin-4-yl-1-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-5,6-dihydro-1H-pyridin-2-one CAS545445-44-1 Manufacturer,Supplier](/uploadfile/202108/25/6fe8c67df16dd24299b46e8bf5c30ffa_small.jpg) 3-Morpholin-4-yl-1-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-5,6-dihydro-1H-pyridin-2-one CAS545445-44-1Pharmaceutical intermediates
3-Morpholin-4-yl-1-[4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]-5,6-dihydro-1H-pyridin-2-one CAS545445-44-1Pharmaceutical intermediates -
![China Acetic acid, 2-chloro-2-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazinylidene], ethyl ester CAS27143-07-3 Manufacturer,Supplier](/uploadfile/202108/25/b3b86c72de9928dc32b024d1f767bce8_small.jpg) Acetic acid, 2-chloro-2-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazinylidene], ethyl ester CAS27143-07-3The pp shaaban intermediates
Acetic acid, 2-chloro-2-[2-(4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazinylidene], ethyl ester CAS27143-07-3The pp shaaban intermediates
 86-15062454963
86-15062454963 sales@yacoo.com.cn
sales@yacoo.com.cn











